What is underpinning?

Underpinning is a method for strengthening and repairing of building foundations. So, here it is discussed about underpinning methods, what is underpinning, selection of underpinning methods, types of works of underpinning methods selection, structural conditions which requires underpinning and need for underpinning. There are circumstances where a disappointment in foundation or footing happens surprisingly after the fulfillment of entire structure i.e., both the substructure and superstructure.
Under such a crisis circumstance a remedial method must be recommended to recover the structural stability. The underpinning method helps to reinforce the structural foundation of a current structure or other infrastructures. These include establishment of extremely durable or impermanent help to a generally held foundation with the goal that extra profundity and bearing capacity is accomplished.
Selection of Underpinning Methods
Underpinning methods are chosen dependent on time of structure and types of works included. The structure classifications dependent on its ages are:
- Ancient Structures: Ages greater than 150 years.
- Recent Structures: Ages between 50 to 150 years.
- Modern Structures: Ages under 50 years.

Types of Works for Underpinning Methods Selection
- Conversion Works
- Protection Works
- Remedial Works
Conversion Works
The structure must be changed over to another capacity, which requires more grounded foundation contrasted with existing
Protection Works
The accompanying issues of a structure needs to go through protection works:
- The existing foundation isn’t solid or stable.
- Nearby removal would influence the soil that supports existing footing.
- Stabilization of the foundation soil to oppose against normal disasters.
- Requirement of storm cellar under an all around existing structure.
Remedial Works
- Mistakes in beginning foundation design caused subsidence of the structure.
- Work on present structure than building another one.
Structural Conditions which Requires Underpinning
There are several reasons for which an engineer needs to recommend underpinning method for adjustment of substructure, such as,
- The debasement of timber piles utilized as a foundation for typical structures would cause settlement. This debasement of structures is because of water table variances.
- Rising and bringing down of the water table can cause a reduction of bearing capacity of soil making the structure to settle.
- Structures that are worked over soil with a bearing capacity not suitable for the structure would cause settlement.

Need for Underpinning
The choice of underpinning necessity can be mentioned dependent on observable facts. At the point when an all around existing structures begin to show certain change through settlement or any sort of distress, it is important to build up vertical level readings just as at the offset level, on an ideal premise. The time-frame relies on the, how extreme is the settlement.
Presently, before the exhuming for another undertaking, experts need to intently look at and decide the soil capability to oppose the structure that is coming over it. In light of that report the need for underpinning is chosen. Some of the time such test would try not to support to be done after the entire structure is developed.
Underpinning Methods
Following are the diverse underpinning methods utilized for foundation reinforcing:
- Mass Concrete Underpinning Method (Pit Method)
- Underpinning by Cantilever Needle Beam Method
- Pier and Beam Underpinning Method
- Mini Pilled Underpinning
- Pile Method of Underpinning
- Pre-Test Method of Underpinning
Whatever be the types of underpinning methods chose for reinforcing the foundation, every one of them follow a comparable thought of expanding the current foundation either longwise or breadthwise and to be laid over a more grounded soil stratum. This empowers conveyance of load over a more prominent region. Diverse underpinning methods are referenced momentarily in the accompanying areas. The decision of underpinning methods relies upon the ground conditions and the necessary foundation profundity.
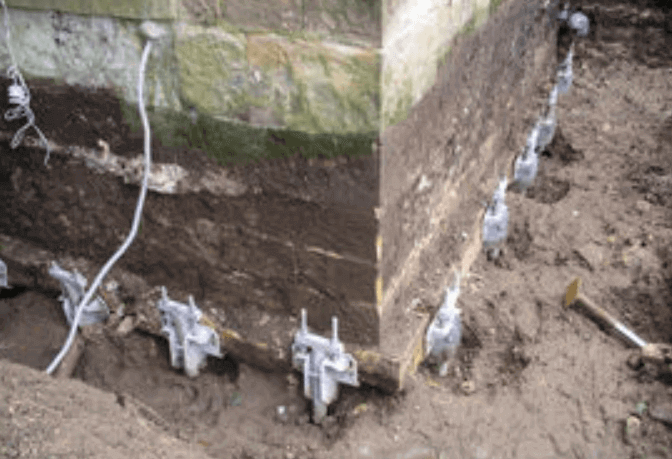

Mass Concrete Underpinning Method (Pit Method)
Mass concrete underpinning method or the pit method is the traditional underpinning methods, as it has been trailed by hundreds of years. The method includes broadening the old foundation till it arrives at a stable stratum. The soil underneath the current foundation is uncovered in a controlled way through stages or pins. At the point when strata suitable is reached, the unearthing is loaded up with concrete and saved for curing, before next removal begins.
To move the load from old foundation to new one, another pin is given through setting dry sand-cement pack. This is a minimal expense method suitable for the shallow foundation. For more convoluted issues identified with the foundation other better methods have than pick.
Underpinning by Cantilever Needle Beam Method
The underpinning by cantilever needle beam method in generally an extension of pit method. In case if the foundation must be stretched only to one side and the plan have a grounded column inside then this method can be utilized for underpinning.
Advantages of Cantilever Needle Beam Method
- It is faster than traditional method.
- It has only one side access.
- It has high load carrying capacity.
Disadvantages of Cantilever Needle Beam Method
- Digging discovered uneconomical while existing foundation is profound.
- Constraint in access limits the utilization of needle beams.

Pier and Beam Underpinning Method
It is additionally named as base and beam method which was executed after Second World War. This method advanced on the grounds that the mass concrete method couldn’t function admirably for a tremendous profundity of foundation. It is found possible for the greater part of the ground conditions. Here reinforced concrete beams are set to move the load to mass concrete bases or piers. The size and profundity of the beams depend on the ground conditions and applied loads. It is found practical for profundity shallower than 6.0 m.
Mini Piled Underpinning
This method can be carried out where the loads from the foundation need to moved to strata situated a ways off more noteworthy than 5.0 m. This method is adaptable for soil that has variable nature, access is prohibitive and causes environmental pollution issues. Piles of diameter between 150 – 300 mm in diameter is driven which might be either forecast or driven steel cased ones.
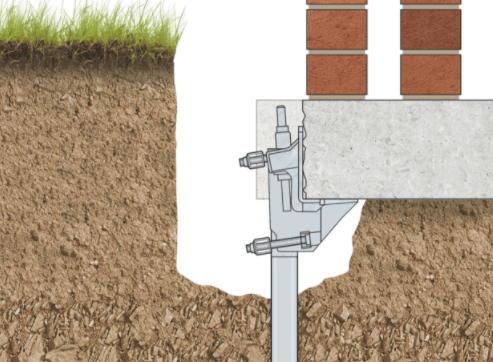
Pile Method of Underpinning
In this underpinning methods, piles are driven on adjacent sides of the divider that upholds the feeble foundation. A needle or pin infiltrates through the divider that is thus associated with the piles. These needles act like pile covers. Settlement in soil because of water clogging or clayey nature can be treated by this method.
Pre-test Method of Underpinning
It is utilized for pad or strip foundation. It can be utilized for working with 5.0 – 10 stories. Here the subsoil is made compact and compressed, in the new removal level that gives foreordained loads to the soil. This is done prior to underpinning method is performed. Here diminished clamor and interruption are normal. This method can’t be executed for raft foundation.
So, here it is discussed about what is underpinning, selection of underpinning methods, types of works of underpinning methods selection, structural conditions which requires underpinning, need for underpinning and underpinning methods.
Types of Foundation in Construction
Bridge Foundation Construction Process and its Types
For more information click here.