Introduction

The water requirement of crops is very important for every single crop that requires water after some fix time till its development. The elements of soil moisture in plant development are vital. Water and nutrients are the two most significant requirement of the crop. Accurate water requirement of crops evaluation is a critical component for right water the board. Such evaluation requires explicit instrumentation, bringing about a troublesome assignment, particularly when woody crops are dissected.
Accordingly, systems for evaluating water requirement of crops differ from basic water balance approaches and crop coefficients to complex energy balance approaches utilizing far off detecting procedures. Notwithstanding, these systems reduce exactness essentially when applied to orchards, requiring explicit devices for adapting to reductions in precision. The primary trouble is identified with the heterogeneity of fields; canopy and uncovered soil generate critical contrasts in evaporation and transpiration, and afterward require the partition of the two terms.
Apparatuses, for example, twofold source models could address this limit, in spite of the fact that information requirements are unreasonably raised for enormous scope and common-sense examination. This requirement is applied either normally by precipitation or falsely by irrigation. Thus, the water requirement of crops incorporates all misfortunes like:
- Transpiration misfortune through leaves.
- Evaporation misfortune through soil surface in cropped region.
- Amount of weather utilized by plants for its metabolic exercises which is assessed as under 1% of the all-out water retention. These three components can’t be separated so without any problem. Subsequently the ET misfortune is taken as crop water use or crop water wasteful use.
- Other application misfortunes are conveyance misfortune, percolation misfortune, runoff misfortune, and so forth.
- The water required for unique purposes like puddling activity, furrowing activity, land readiness, draining, requirement, for the reason of weeding, for dissolving fertilizer and chemical, and so forth.
The principal functions of water requirement of crops are, for example,
- It goes about as a solvent for the nutrients. Water likewise shapes the arrangement of the nutrients and this arrangement is consumed by the roots. In this way, water goes about as the supplement transporter.
- Irrigation water supplies moisture which is fundamental for the chemical activity inside the plant prompting its development.
- Water cools the soil and the atmosphere, and in this manner makes more great climate for sound plant development.

Low Water Requirement Crops
Plants that require low levels of water are regularly called drought tolerant. Drought-open minded plants can flourish in hot, dry conditions with almost no water. They incorporate the two perennials and annuals. Most drought-lenient plants possibly must be hand-watered when they are planted and keeping in mind that they are securing themselves. From that point forward, they can be passed on to the regular pattern of the components. Well known drought open minded trees incorporate the red cedar, live oak, crape myrtle, and the windmill and saw palmetto palm trees.
All citrus trees are additionally drought open minded. Numerous mortgage holders in regions inclined to drought, like pieces of the southern United States, use bushes and ground covering plants as a feature of their finishing. These incorporate Texas wise, orange jasmine and Chinese wellspring grass. There are relatively few perennial drought-open minded plants, yet amaryllis is one that is extremely well known, alongside the African iris. Mainstream drought-lenient annuals incorporate marigold, universe and the Dahlberg daisy.
Mid-Level Water Requirement Crops
Most plants land in this reach with regards to water requirements. These plants don’t should be watered each day, however they should be watered when the soil has been dried for longer than possibly 14 days. Now and again these plants are named plants lying in “an intermittent water zone”. These incorporate famous plants, for example, geraniums, most roses, wisteria, clematis and other plant plants, sunflowers, spring blossoming bulbs, and most blooming perennial bushes. Note that blossoming annuals planted in holders will require watering to some degree more than once per week, while annuals planted in the ground will require watering less regularly.
High Water Requirement Crops
A few plants require a lot of water. These plants commonly fill in muddy regions or marshes, or along the banks of rivers, streams and lakes. The soil for these plants ought to consistently be kept sodden. Standing water isn’t a worry for these plants, so you don’t need to stress over root decay. Perennials are particularly useful for wet regions since they don’t need to be replanted quite a long time after year, which can be troublesome in muddy regions.
Well known perennials for wet soil incorporate iris plants, cannas, honey bee emollients, greeneries, and lowland salvia. Amphibian mint is a wonderful ground cover that preferences wet soil. Most annual blossoming plants additionally well in continually damp soil.
Estimating the Water Requirement of Crops
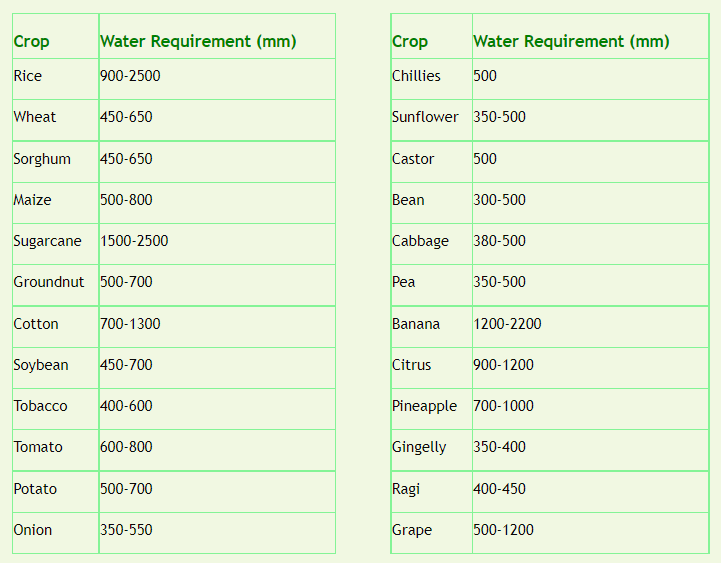
The estimations of the water requirement of crops are one of the essential requirements for crop anticipating the ranch and for the arranging of any irrigation project. At the point when future environment conditions are considered for the estimation of water requirement of crops, reenactment models have an uncommon pertinence, as they are the interesting methodologies ready to reproduce future crop conduct, however consistently after an adjustment and approval technique dependent on test information.
ET0 addresses the most extreme, or potential, evapotranspiration rate that can happen. In any case, the water requirement of the crops is typically under ET0, as there are factors of the actual crop that must be considered. These incorporate the development phase of the plant, the leaf inclusion that gives shade to the ground, and different points of interest of the crops that cause them to fluctuate from one another.
With these factors considered, ET0 is changed over into ETc, through the crop-explicit coefficient, Kc. Under standard conditions ETc tends to evapotranspiration rate of crop. While ascertaining ETc, one should recognize the development phases of the crop, their length and select the legitimate Kc coefficient that should be utilized.
ETc = Kc x ET0
Climatic impacts are incorporated into ET0, while the impact of the crop attributes is incorporated into Kc. The center of any recreation model for yield and irrigation requirements evaluation should be founded on crop transpiration estimation.
Example for crop water requirement calculation:
Crop: potato
Development stage: Initial development
Kc for initial stage: 0.45
ET0 (measured by a neighborhood meteorological station): 9 mm/day
Therefore, ETc = Kc x ET0 = 0.45 x 9 = 4.05 mm/day
Factors Affecting Water Requirement of Crops

- Water Table: If the water table is closer to the ground surface, the water requirement will be less. In case it is much beneath the ground surface, the water requirement of crops will be more.
- Climate: In warm climate, the evaporation misfortunes more and henceforth the water requirement of crops will be more and the other way around.
- Ground Slope: If the slope of the ground is steep, the water streams down rapidly and the soil gets brief period to retain imperative moisture bringing about water misfortune. In this way, the water requirement of crops will be all the more however in the event that the ground is level, the water streams gradually and the soil gets sufficient opportunity to retain the adequate moisture. Along these lines, the water requires is less.
- Intensity of Irrigation: If the intensity of irrigation for a specific crop is high then more region goes under the irrigation framework and the water requirement of crops is more and the other way around.
- Type of Soil: In sandy soil water permeates rapidly and can’t be held. In this way, the water requirement of crops is all the more however the clayey soil can hold water close to the root zone of the crops, so it requires less water.
Optimum Use of Water
During the development time of the crop the amount of water provided to a specific crop giving greatest yield of the crop is called optimum water requirement. To get the most extreme crop yield the information on optimum water requirement of crops are fundamental. In the event that the inventory of water to the crop is pretty much than its optimum requirement, it will antagonistically influence the crop yield. Consequently, for the greatest crop yield it ought to be provided with optimum amount of water.
Scope of Irrigation Engineering
For more information click here.