What is WBM Road?

The Water Bound Macadam (WBM) Roads which is the most ordinarily utilized road construction procedure for over 100 years. The Water Bound Macadam is named based on the Scottish engineer, Sir John Macadam who initially presented and construct the WBM roads. He was the Surveyor General of Roads in England. Macadam set forward an altogether new method for road construction.
Water Bound Macadam Road is a kind of flexible pavement where base and surface layer contains broken rock pieces or crushed stones and materials are interlocked with the help of a roller. Then, the voids are stacked up with the help of binding materials and screening materials close by water and compaction.
In Water Bound Macadam, the quantity and thickness of each compacted layer depends on the loading and design thought. Notwithstanding, they generally differ from 7.5 cm to 10 cm thick. The Water Bound Macadam layers can undoubtedly deteriorate because of moving vehicle loads and surface water, accordingly the surface layer is typically disallowed to furnish with the WBM layer. The road camber of 1 out of 36 to 1 out of 48 is generally ideal in WBM roads.
Types of Macadam Road
- Water Bound Macadam
- Traffic Bound Macadam
- Bituminous Macadam
- Cement Macadam
WBM Road Cross Section
The following drawing describes the WBM road cross section.
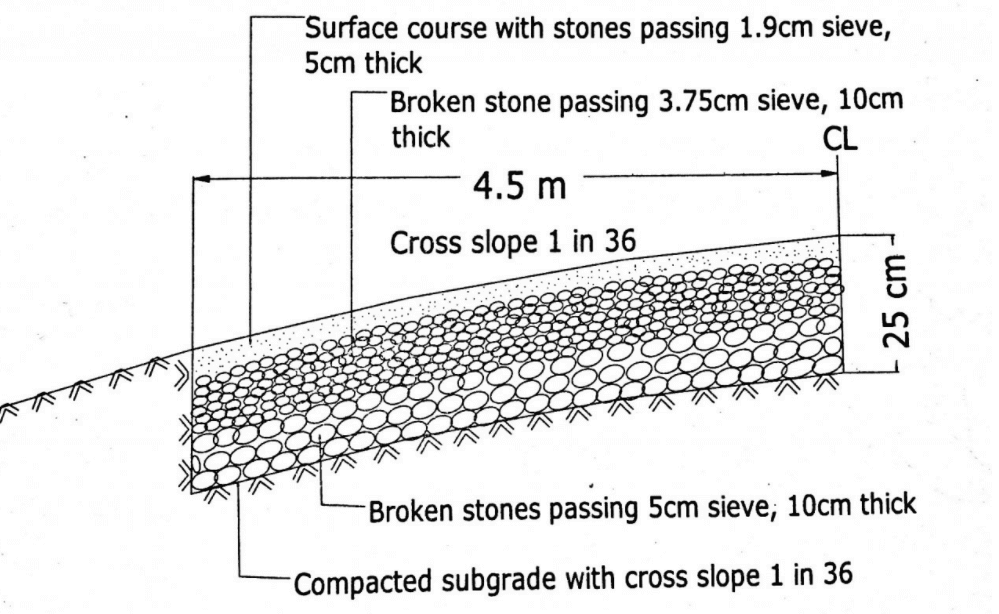
Macadam Road Construction Method
- Macadam perceived the significance of subgrade, drainage and compaction, henceforth gave a cross slope.
- He recommended that weighty foundation stones were not in any way important to be put at the lower part of the road.
- The compacted layer of broken stones is put at the base.
- The subgrade ought to be appropriately depleted.
- Though the thickness of the road was not exactly past methods, yet WBM roads served better because of load scattering attributes.
Materials Required for WBM Road
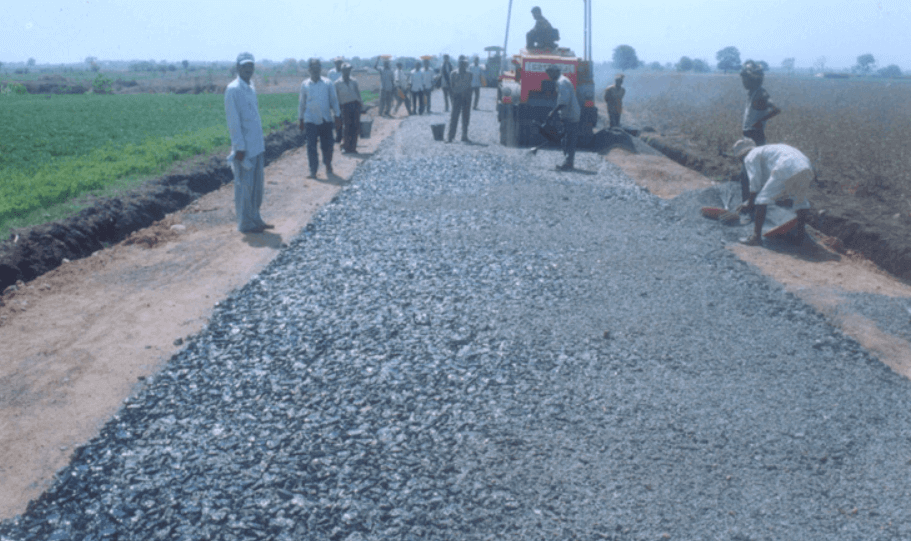

There are mainly three sorts of construction material are needed for the construction of WBM roads:
- Coarse Aggregate
- Screening
- Binding Material
Coarse Aggregate
Coarse aggregate is comprising of a mixture of hard and durable crushed aggregate and broken stones. The aggregates utilized for each layer of the WBM roads construction ought to be very much graded. For each layer of the WBM roads construction the aggregates utilized are ought to be very much graded.
The coarse aggregates utilized in the construction of WBM roads ought to have the accompanying properties:
- It ought to be strong, hard and durable.
- It ought not have exorbitant measure of elongated and flaky particles.
- It ought to be fit as a fiddle and size as displayed in the gradation table.
Screening
To fill up the spaces or voids left between aggregate particles after the compaction is finished a construction material called screening is utilized in WBM roads construction work. Generally, construction materials utilized for screening purposes have more modest sizes contrasted with coarse aggregate. To lessen the general expense of WBM roads, IRC (Indian Road Congress) has suggested utilizing non-plastic materials, for example, kankar, murram, or gravel as opposed to screening.
Binding Material
A Binding Material that will be used for the WBM roads ought to be checked and approved by the functioning engineer and it ought to have least plasticity. Generally, the Index value is restricted to 6. In some cases, the Binding Material isn’t needed in case the screening is used in the construction of crushed rocks or WBM roads as they have crushable property.
Construction Procedure of WBM Road

- Foundation Preparing for Receiving WBM Course
- Lateral Confinement of Aggregates
- Spreading Coarse Aggregates
- Rolling
- Applications of Screenings
- Sprinkling and Grouting
- Application of Binding Materials
- Setting and Drying
Foundation Preparing for Receiving WBM Course
The foundation that is supporting the layer of Water Bound Macadam is either the sub-base or subgrade course. It is ready to the necessary grade and chamber. It is cleaned of all the dust particles and free materials present on it. The foundation supporting the WBM ought to be dried. At the point when the current road is topped dark, furrows are cut at a time period at an angle of 45 degree to the middle line of carriageway.
Lateral Confinement of Aggregates
The aggregates are confined in WBM roads since, assuming that they are put on the subgrade and there are possible outcomes of aggregates might come out because of the traffic loads. It is completed by the construction of shoulders of thickness similar to the thickness of the compacted layer of Water Bound Macadam, that is of 7.5cm.
Spreading Coarse Aggregates
The aggregates ought to be evenly and uniformly spread on the pre-arranged base in the necessary sum. They might be spread physically or precisely. The thickness of the layers of WBM constructed ought to be more than 75mm.
Rolling
When the aggregates are spread evenly the rollers are conveyed to do the course of compaction. The roller utilized will be of 6 to 10 tons limit. The compaction of aggregates should begin from the edge of the surface. The aggregates are compacted somewhat then the compaction is stopped to allow the applications of screenings.
Application of Screening
After somewhat compaction of aggregates, screenings are applied so the voids in the aggregates are filled totally. They are applied progressively over the surface in at least three applications. Once more, in the wake of applying screenings, dry rolling is continued with the goal that they are totally made up for in the shortfalls.
Sprinkling and Grouting
The surface is sprinkled with water in the wake of applying the screenings. The surface is then cleared and rolled so the voids are totally filled. In the event that any voids are left unfilled, extra screenings might be applied.
Application of Binding Materials
Subsequent to applying the screenings, binding materials are applied in dainty layers. At least two flimsy layers of covers are applied. After the applications of each layer of binding materials, water is sprinkled trailed by compaction of layers by rollers of 6 to 10 tons limit.
Setting and Drying
After all the previously mentioned measures, the layer of WBM is permitted to set for the time being. Following day the road is investigated and if any voids are vacant, they are filled and compacted.
Maintenance of WBM Road

- If any sort of potholes or rugs spotted on the recently constructed WBM roads, within a brief period, the concerned authority should fix it by filling it with necessary materials and setting the materials on potholes ought to be done appropriately.
- To restricted aggregate from getting free from the surface course of the road, a slender layer of clammy soil ought to be spread over the surface occasionally, especially after the rainy season.
- The lopsidedness that happened should be eliminated from the constructed road through hauling. It might cause the circumstance all the more gravely for the constructed roads.
- Fresh materials ought to be utilized instead of any broken materials on the constructed road.
- Every 2 to 5 years after the tightening, the surface of the constructed road needed to be restored, keeping in see the volume of traffic.
- After the road opens for traffic, the free mixture should be taken out that comes on the highest point of the road surface. Alongside the crisp binding material, the evened out road surface ought to be added and it ought to be appropriately compacted and watered.
- The dust issue can be successfully taken out by giving a surface dressing of bituminous materials.
Advantages of WBM Roads

- It is practical as the expense of construction of Water Bound Macadam Road is similarly low.
- In the construction of the WBM road, no gifted workers are required.
- Water Bound Macadam roads are constructed with the assistance of locally and effectively accessible materials.
- If WBM roads are kept up with consummately every now and then they could oppose substantial traffic and roughly around 900 tons each day.
Disadvantages of WBM Roads

- The maintenance cost of Water Bound Macadam Road is high when contrasted with the bitumen base course.
- The in general life expectancy of Water Bound Macadam Road is not exactly the bitumen road.
- A high likelihood of risk to traffic and burden is there if these roads don’t get legitimate maintenance intermittently.
- These roads lead to yielding and mellowing of the subsoil as these roads are permeable to rainwater.
- When a quick vehicle ignores a WBM roads, the stone piece gets upset lastly, the road surface crumbles.
For more information click here.
Pingback: 7 Types Of Scaffolding | What Is Scaffolding? | Parts Of Scaffolding | CivilString