The term chain surveying in survey work refers to measurement of distances with the chain or a tape. Amongst different types of land surveying, the chain surveying is one of them. In chain surveying the linear measurements are only made, and no angular measurements are taken in this type of surveying. Here it is discussed about what is chain surveying, principles of chain surveying, types of chain in surveying, chain surveying instruments, procedure of chain surveying and chain surveying diagram.
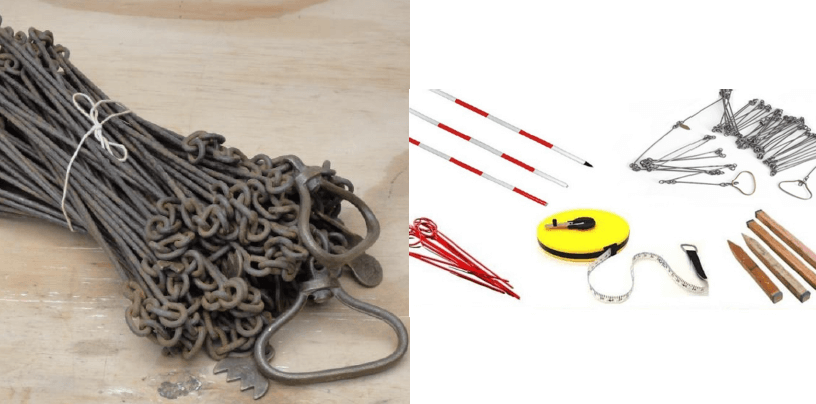

What is Chain Surveying in Civil Engineering?
Chain survey is suitable for the survey of areas that are fairly flat and small areas with simple details. This method is generally known as chain surveying because the principle instrument or equipment used in this method is the chain. The term taping can also be used for measurements with a tape. Tapes are more accurate and easier to carry and use than chains. However, chain surveying is ideally suited for rough use in difficult terrains.
For every surveyor it is necessary to measure horizontal distance between two points on earth surface. The horizontal distances can be measured by many methods, out of which, using a chain or a tape is the most common. The SI unit of distance is meter, which is used to measure small distances. Large distances can be measured in multiples of this unit such as, kilometer (km). Very small distances can be measured in sub-multiples such as, millimeter (mm) and centimeter (cm). In regular survey works, the unit meter is commonly used. If the lengths or distances are specified in other system of units, they are converted into SI units by using standard conversion factors.
Principle of Chain Surveying
- The main principle of chain surveying is to divide the survey plot into small survey areas by triangulation method.
- Measure the lengths and angles with tape and compass respectively.
- The measurements are used so that the surveyed drawing can be plotted on paper.
- The chain survey is also known as chain triangulation, since the triangulation method is the principle of chain surveying.
- The triangles that are formed by the triangulation method should resemble with an equilateral triangle shape.
- The formed triangle should be a well-conditioned triangle and those are almost equilateral in shape are known as well-conditioned triangles.
- If there is a triangular survey area and sequence and lengths of its three sides are noted, then the plan of the survey area can be drawn easily.
- If the survey area includes more than three straight boundaries then it’s no longer enough to measure side lengths completely.
- The field measurements should be excessively organized such that the region can be plotted by setting down triangles and different plans ought to be ready to fulfill the condition.
Types of Chain in Surveying
The following are the different types of chain in surveying that are commonly used:
- Metric Chain
- Surveyor’s Chain or Gunter’s Chain
- Engineer’s Chain
- Revenue Chain
- Steel Band or Band Chain
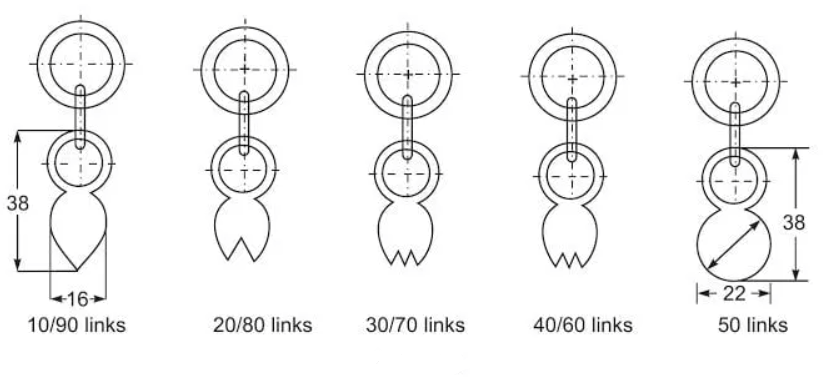
Metric Chain
Metric chains are generally available in the lengths of 5 m, 10 m, 20 m and 30 m. In this types of chain in surveying, tallies are fixed at each meter length of 5 and 10 meter chain and each 5 meter length for chains of 20 meter and 30 meter length, so as to enable fraction readings a chain with less trouble. At every meter there is a small brass ring provided, except the places where the tallies are attached.
Surveyor’s Chain or Gunter’s Chain
A Surveyor’s chain or a Gunter’s chain length is 66 feet and consists of 100 links, each link being 0.66 feet or 7.92 inch in length. In this types of chain in surveying the length of 66 feet was adopted for convenience in length measurement, has 10 sq. chains are equal to 1 acre. Also when linear measurements are required in furlongs and miles, these chain is more convenient as 10 chains make 1 furlong and 80 chains make 1 mile.
Engineer’s Chain
An engineer’s chain is 100 feet in length and consists of 100 links, each link being 1 feet long. In this types of chain in surveying a brass tag is attached at every ten links with notches on the tags that are demonstrating ten link segments number between tags and end of the chain.
Revenue Chain
The revenue chain is 33 feet in length and consists of 16 links each links being 2*1/16 feet long. This types of chain in surveying is used for measuring fields in cadastral survey.
Steel Band or Band Chain
These kinds of chain comprise of a long thin portion of steel of uniform width of 12mm to 16mm and thickness of 0.3mm to 0.6mm. This chain is partitioned by brass studs at each 20cm or rather than brass studs, band chains might have graduated etching as centimeter. In this types of chain in surveying, for simple use and workability band chains are twisted on steel crosses or metal staggers from which they can be handily unrolled. These steel bands are accessible in 20m and 30m length and the width of around 12mm to 16mm.
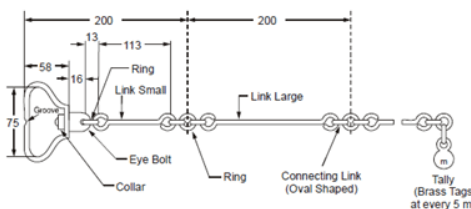
Chain Surveying Instruments
The chain surveying instruments that generally used are:
- Chains
- Tapes
- Wooden Peg
- Arrow
- Ranging Rod
- Ranging Pole
- Offset Rod
Chains

Chains are the formation of straight links made of galvanized mild-steel wires and bent up into rings at the steel wire ends. These bent up rings are then joined with three small circular rings. The swivel joints are provided at the ends of the chain, so that without twisting the chain can be turned. A surveying chain link length is the distance between two consecutive middle ring centers, while the surveying chain length is measured from the one handle outside to the other handle outside.
Tapes
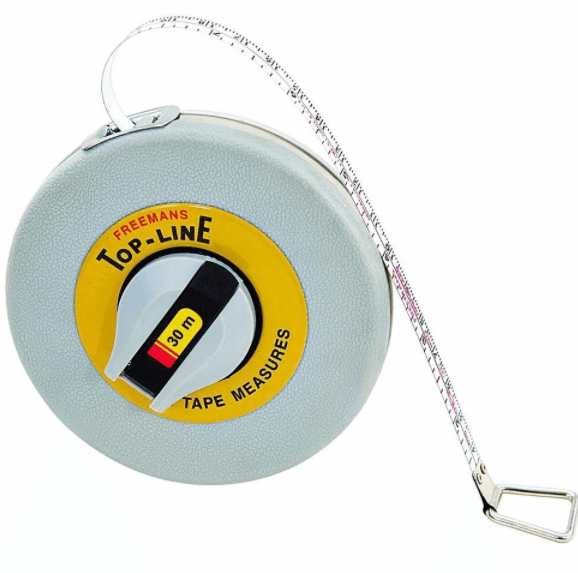

There are different types of tapes that are available based on lengths, materials and weights. The following are the different tapes that are used in survey.
- Cloth or Linen Tape: Tapes made of cloth or linen are used for taking offset measurements. These are available in lengths of 10m-30m and widths of 12m – 15mm. However, they find little use in survey due to their tendency to stretch and twist when wet.
- Metallic Tape: Metallic tape is made of yarn and metallic wires. They come in lengths of 2, 5, 10, 20, 30 and 50 meters. Longer tapes have a metal ring attached at the outer end of the tape, which is fastened to the tape by a metal strip of the same width as the tape. The outer end is also reinforced by leather or plastic for a length of 10cm, where the tape length includes the metal ring. The width of the tape is usually 16mm. The tape is also graduated and membered to centimeters in black. The meter markings are numbered and the lines extend to the full width of the tape. The meter markings are numbered in red.
- Steel Tape: Metric steel tapes are 6mm to 10mm in width. The tape is made of steel or stainless steel, and may have a protective vinyl coating to prevent rust. The tape has a metallic ring attached, the outer end of which is the zero point of the tape. The tape is suitably marked in meters, decimeters and centimeters. The outer end of the tape may also be marked in millimeters.
- Invar Tape: Invar tape is made of an alloy of 36% nickel and 64% steel. These are available in lengths of 30m, 50m and 100m. The width of the tape is 6mm and it is graduated to millimeters throughout its length. It is very delicate and therefore it requires careful handling. It is used for high-precision works.
Wooden Peg
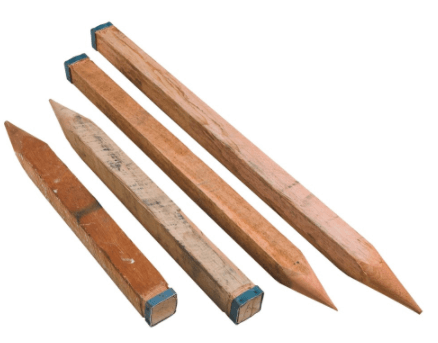
Wooden pegs are used for marking stations. They are generally 150mm – 200mmin length and have a cross-section of 625 – 2500 mm2. These wooden pegs are tapered at one end so that it can be hammered by a wooden hammer to drive them into the ground. Wooden pegs of longer lengths and heavier sections are also used depending on the ground conditions.
Arrow

Arrows are very essential for chaining distances. They are made of 4mm diameter steel wires, about 400mm in length. The wire is bent into a hook or a ring and one end, and tapered to a point at the other. The ring assists in carrying the arrow while the pointed end helps in driving it into the ground. Usually, a set of 10 arrows is carried with a chain and inserted at the end of chain length.
Ranging Rod
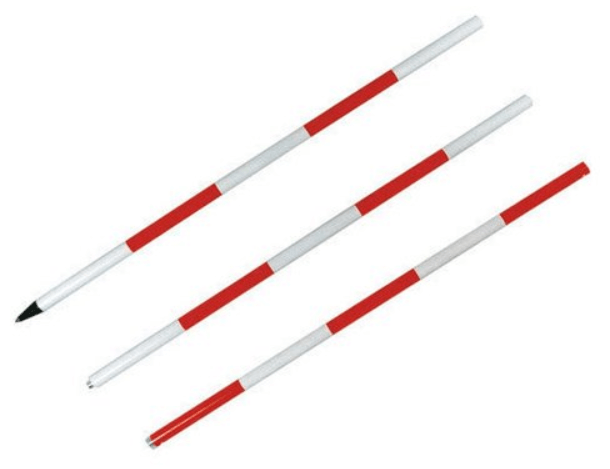

Ranging rods are used for ranging. They are made of well-seasoned wood of deodhar, pine, sissoo and other similar variety of woods. They come in lengths of 2m or 3m, and generally have a circular cross-section, 30mm in diameter. They are painted in alternate bands of white and red or white and black. The bands are 200mm in width. The lower ends of ranging rod is provided with a steel shoe for a length of 150mm to protect the rod from wear and tear. Ranging rods are used for ranging and for marking stations for the purpose of indivisibility and ranging.
Ranging Pole
Ranging poles serve the similar purpose as the ranging rods, except they are longer in 4 – 6 m in length with the diameter varying from 60mm to 100mm. For distinctiveness and visibility, they two are painted in alternate bands of white and red or white and black.
Offset Rod
Offset rods are used to measure short offsets. They are similar in construction to ranging rods, but are longer and have the larger process. Offset rods are generally 3m in length, divided into 200mm sections, and painted in alternate bands of black and white. They have iron shoes at the bottom and may be provided with a hook or notch on one side to pull or push the chain. They may also have rectangular holes running through the right angles to help aligning offsets and right angles.
Procedure of chain surveying
- The first step of chain surveying procedure is to inspect the area that is needed to be surveyed and then prepare an index map or a rough sketch. This step is known as reconnaissance phase.
- After the completion of the first step, the stations are marked by driving pegs or wooden pegs, ranging rods or ranging poles to fix the stations.
- After that, the main line is passed following the specified way and passes through the center of the ground.
- The next step is to fix the ranging rods on the stations.
- After following the previous steps, the chaining process can begin.
- Make ranging on the ground wherever it is necessary.
- Lastly, take the offsets and measurements of changes and record the observations duly in the field book.
Chain Surveying Diagram
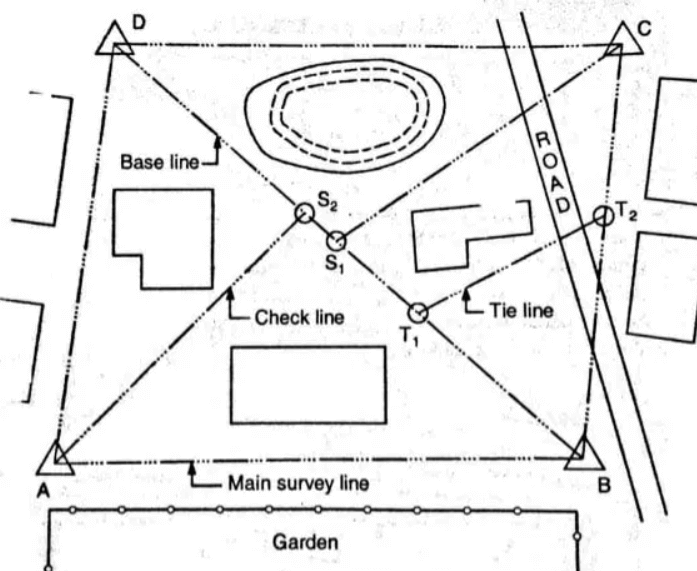
So, here it is discussed about what is chain surveying, principles of chain surveying, types of chain in surveying, chain surveying instruments, procedure of chain surveying and chain surveying diagram.
FAQ >
Q. Name the different types of instrument used in chain surveying stating their use.
Ans: The different types of instrument used in chain surveying are chains, tapes, wooden pegs, arrows, ranging rods, ranging poles and offset rods.
Q. Intro to surveying chain surveying.
Ans: The term chain surveying in survey work refers to measurement of distances with the chain or a tape and chain surveying is used for difficult terrains.
Q. Is code relevant for chain surveying?
Ans: Generally, code is not relevant for chain surveying, but in some cases of the measurements and areas, codes are helpful.
Q. What are the points to be borne in mind in arranging the survey lines in chain survey?
Ans: The points to be borne in mind in arranging the survey lines in chain survey are such as,
- Mutually intervisible stations should be present.
- Possible lines should be drawn of the whole area and principles of chain surveying should be observed.
- In each triangle, a check line is must and there should be well defined triangles.
- There should be limited tie lines and survey lines.
- Survey lines position should be in a way to avoid obstacles.
- Survey lines of triangles should pass close to the boundary and should be level ground.
Q. Define chain surveying.
Ans: Chain surveying refers to measurement of distances with the chain or a tape in difficult terrains.
Q. In chain survey field work is limited to –
Ans: Linear measurements only.
You Might Like >
Triangulation Method in Surveying
For more information click here.